7.1 KiB
Running Applications
Application Structure
The basic application that you just installed is organized as follows,
basic/ application base path
assets/ contains asset bundles
commands/ contains console commands
config/ contains application configurations
controllers/ contains controller classes
mail/ contains views for mail messages
layouts/ contains layouts for mail messages
models/ contains model classes
runtime/ contains files generated during runtime, such as logs, cache files
views/ application view base path
layouts/ contains layout files
site/ contains view files for the site controller
web/ application Web root
assets/ contains published asset files by Yii, such as css files, js files
css/ contains CSS files
The basic application template includes four pages: a homepage, an about page, a contact page, and a login page. The contact page displays a contact form that users can fill in to submit their inquiries to the webmaster. Assuming the site has access to a mail server and that the administrator's email address is entered in the configuration file, the contact form will work. The same goes for the login page, which allows users to be authenticated before accessing privileged content.
Root directory contains a set of files.
.gitignorecontains a list of directories ignored by git version system. If you need something never get to your source code repository, add it there.codeception.yml- Codeception config.composer.json- Composer config described in detail below.LICENSE.md- license info. Put your project license there. Especially when opensourcing.README.md- basic info about installing template. Consider replacing it with information about your project and its installation.requirements.php- Yii requirements checker.yii- console application bootstrap.yii.bat- same for Windows.
config
This directory contains configuration files:
console.php- console application configuration.params.php- common application parameters.web.php- web application configuration.web-test.php- web application configuration used when running functional tests.
All these files are returning arrays used to configure corresponding application properties. Check Configuration guide section for details.
views
Views directory contains templates your application is using. In the basic template there are:
layouts
main.php
site
about.php
contact.php
error.php
index.php
login.php
layouts contains HTML layouts i.e. page markup except content: doctype, head section, main menu, footer etc.
The rest are typically controller views. By convention these are located in subdirectories matching controller id. For
SiteController views are under site. Names of the views themselves are typically match controller action names.
Partials are often named starting with underscore.
web
Directory is a webroot. Typically a webserver is pointed into it.
assets
css
index.php
index-test.php
assets contains published asset files such as CSS, JavaScript etc. Publishing process is automatic so you don't need
to do anything with this directory other than making sure Yii has enough permissions to write to it.
css contains plain CSS files and is useful for global CSS that isn't going to be compressed or merged by assets manager.
index.php is the main web application bootstrap and is the central entry point for it. index-test.php is the entry
point for functional testing.
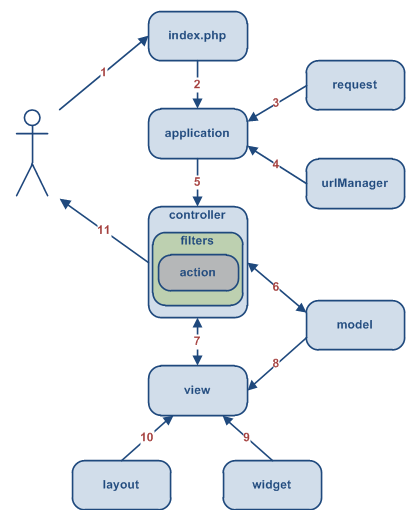
The following diagram shows a typical workflow of a Yii application handling a user request:
- A user makes a request of the URL
http://www.example.com/index.php?r=post/show&id=1. The Web server handles the request by executing the bootstrap scriptindex.php. - The bootstrap script creates an yii\web\Application instance and runs it.
- The Application instance obtains the detailed user request information from an application component named
request. - The application determines which controller and which action of that controller was requested.
This is accomplished with the help of an application component named
urlManager. For this example, the controller ispost, which refers to thePostControllerclass, and the action isshow, whose actual meaning is determined by the controller. - The application creates an instance of the requested controller to further handle the user's request.
The controller determines that the action
showrefers to a method namedactionShowin the controller class. The controller then creates and executes any filters associated with this action (e.g. access control or benchmarking). The action is then executed, if execution is allowed by the filters (e.g., if the user has permission to execute that action). - The action creates a
Postmodel instance, using the underlying database table, where the ID value of the corresponding record is1. - The action renders a view named
show, providing to the view thePostmodel instance. - The view reads the attributes of the
Postmodel instance and displays the values of those attributes. - The view executes some widgets.
- The view rendering result--the output from the previous steps--is embedded within a layout to create a complete HTML page.
- The action completes the view rendering and displays the result to the user.
Application Structure
Note: This section is under development.
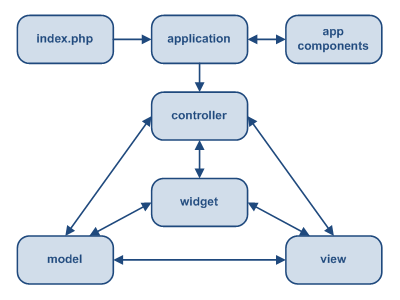
Yii implements the model-view-controller (MVC) design pattern, which is widely adopted in Web and other application programming. MVC aims to separate business logic from user interface considerations, allowing developers to more easily change one component of an application without affecting, or even touching, another.
In MVC, the model represents both the information (the data) and the business rules to which the data must adhere. The view contains elements of the user interface, such as text, images, and form elements. The controller manages the communication between the model and the view, acting as an agent that handles actions and requests.
Besides implementing the MVC design pattern, Yii also introduces a front-controller, called application. The front-controller encapsulates the execution context for the processing of a request. This means that the front-controller collects information about a user request, and then dispatches it to an appropriate controller for the actual handling of that request. In other words, the front-controller is the primary application manager, handling all requests and delegating action accordingly.
The following diagram shows the static structure of a Yii application: